NICOs
Home » Disturbance fields » NICOs
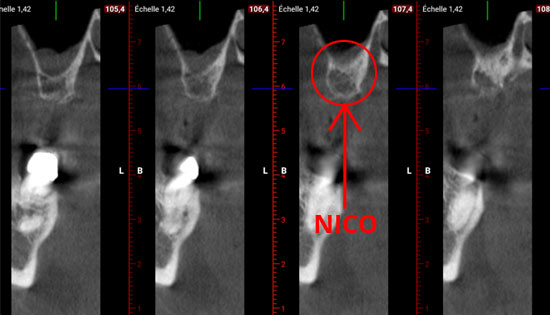
Fatty degenerative osteitis of the jaw (FDOJ), more commonly known on the Internet as NICOs, is a form of ischaemic osteonecrosis which appears to be due to a lack of oxygenation or an infection in an extraction site. Healing is then incomplete.
These osteolyses of the jaw represent a typical field of disturbance and belong to the category of neuromodulatory supports.
They are locally asymptomatic, but the spread of inflammatory mediators (TNF-, IL-1, RANTES) can cause distant problems in the body. More than 73,000 scientific articles study the relationship between RANTES and pathologies such as breast cancer, chronic rheumatic diseases, neuropathies, autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Hashimoto's, etc.
How is FDOJ (NICO) diagnosed?
The diagnosis is based on a study that includes a panoramic radiological examination, followed by an ultrasonic examination using CaviTAU® and a cone beam.
If the blood level of RANTES is higher than 30mg/ml, the inflammation may be considered to be systemic and related to distant pathologies.
